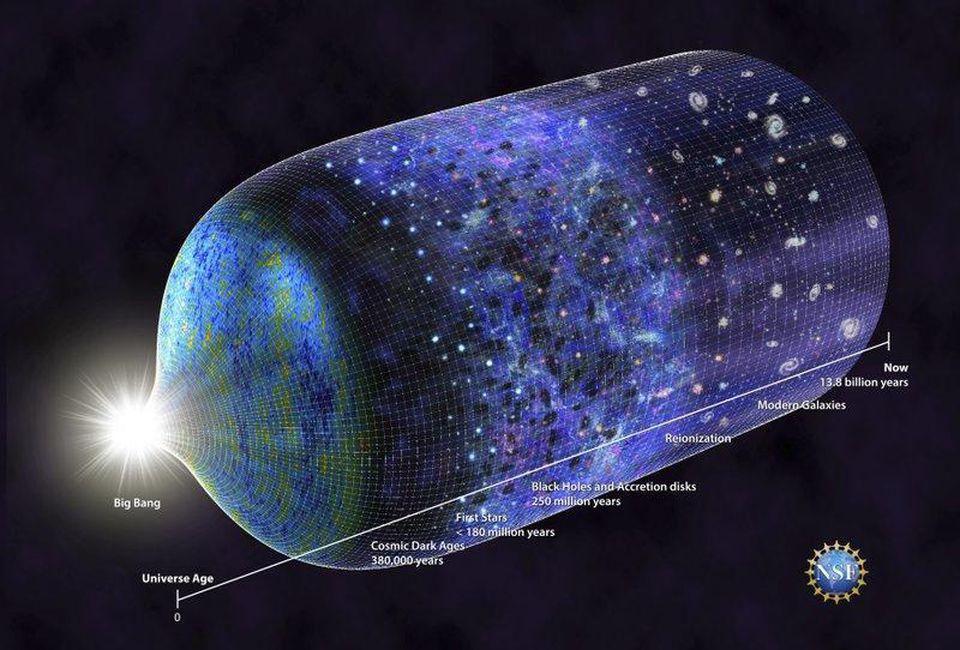
Cynics say that “the only constant is change.” And there is a certain amount of truth to that. Take for example the ever-changing weather. Summer heat gives way to autumn and changing colors. This then gives way to winter cold and snow, which turns into spring and blooming flowers. All these changes occur within a year, and then the cycle starts all over again. On another front, we are exposed to around 100,000 words a day—equivalent to 20 plus words per second through texting, email, the internet, television and other media. This avalanche of information and noise may be the basis for the turmoil in our politics and the topsy-turvy nature of our personal lives. Because change is everywhere, we are more than willing to accept the characterization that it is the only constant in our lives. However, like the turbulent ocean breakers during a stormy day, the apparent turbulence is only on the surface. Diving into the violent sea, the calmness of the deep waters is surprising. Similarly, if we go deeper into the origin and development of the universe, we realize that there is a level of existence where constancy is the rule. In fact, without the unchanging nature of entities, units, values, and interactions, the universe of change would be impossible.
This is the surprising conclusion arrived at by physicists and cosmologists. They point out that many fundamental factors in this universe do not change – EVER. And such stability provides the basis for the turmoil. Physics tells us that it takes 26 dimensionless constants to describe the Universe simply and completely. The similarity in numbers to the 26 letters of the English alphabet is fascinating, for the analogy is useful. These basic units represent the foundational elements, the cosmological primitives, from which EVERYTHING arises.
In 2018, the General Conference on Weights and Measures (CGPM) held a meeting where they agreed on new definitions for the base units of all weights and measures, like the kilogram and the second. The goal was to create standards for measuring things based on fundamental universal constants. This would allow such measures to withstand the test of time and not lose accuracy through contaminations and degradations. These definitions went into effect on May 20, 2019, and most of the world did not take notice of this profound change in our lives.
The newly defined measures include the speed of light in a vacuum (299,792,458 meters/second). It includes Planck’s constant = 6.62607015 x 10 -34 J s, the elementary charge = 1.602176634 x 10-19 C, the Boltzmann constant = 1.380649 x 10 -23 J/K, and Avogadro constant (NA) = 6.02214076 x 1023 mol-1. Not only are these measures more accurate than ever, but as I am describing, they are constant and unchanging.
It is interesting to note that no one really knows why these specific factors are constant in our universe. Nonetheless, constancy is important because it makes the universe possible, predictable and not truly chaotic. Despite how messy and disorganized the world may seem, if we know what forces and factors are involved, we can predict the outcome. Although most of the time we do not know all the forces and factors involved, we can imagine how much wilder and confusing it would be if one second, for example, would be a changing variable. But in this universe, one second is now defined in terms of a universal constant as “the duration of 9,192,631,770 periods of the radiation corresponding to the transition between the two hyperfine levels of the ground state of the caesium-133 atom.” Assuming we understand this, we can breathe more easily that this will NEVER change. At least not until we discover a new physics and a new universe.
Other relevant fundamental universal constants in our universe:
- The fine-structure constant (Aα)
- Electric constant (ε0)
- Mass of six quarks, six leptons, the W, Z, and the Higgs boson
- The mass of the electron (me)
- Ratio of proton to electron mass (mu)
- Gravitational constant (G)
- The ideal gas constant (R)
- Absolute zero
- The Schwarzschild radius (Sch. R)
- The Chandrasekhar limit
- The Hubble constant (H0)
- Omega (Ωω)
- Strong interaction
- Weak interaction
- Electromagnetic interaction
- The cosmological constant (Λ)